Merck Anti-NFκB p50 Antibody
✨AI 추천 연관 상품
AI가 분석한 이 상품과 연관된 추천 상품들을 확인해보세요
연관 상품을 찾고 있습니다...
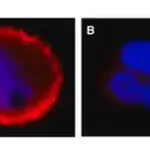
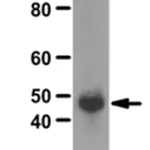
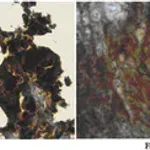
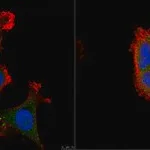
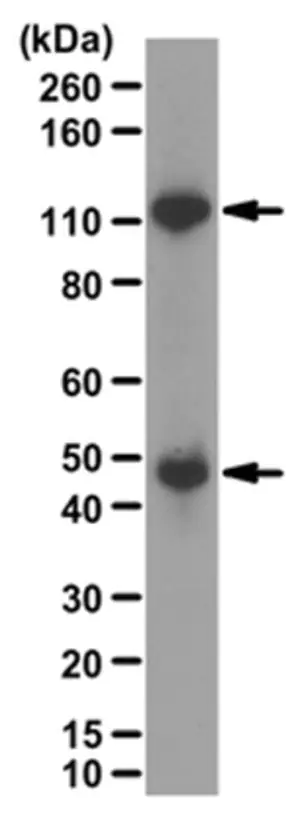
Anti-NFκB p50 Antibody
from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit, NFκB p50, DNA-binding factor KBF1, EBP-1, Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (UniProt P19838; also known as DNA-binding factor KBF1, EBP-1, NF-kappa-B, NF-kappaB, NF-kB1, NFkappaB, NFKB-p105, NFKB-p50, Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit, Nuclear factor kappa-B DNA binding subunit, Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1) is encoded by the NFKB1 gene (Gene ID 4790) in human. NF-κB is a protein complex that plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection/inflammation. NF-κB1 is synthesized as a 968 a.a protein (p105), which undergoes posttranslational processing to generate the p50 subunit (a.a. 1-433). The p50 NF-κB participates in target gene transactivation by forming heterodimers with RelA, RelB, or c-Rel. In addition, p50 homodimer can bind the nuclear protein Bcl-3 and form a functional transcriptional activator complex. In unstimulated cells, the NF-κB dimers are sequestered in the cytoplasm by the family of IκB (Inhibitor of κB) proteins (IκBα, IκBβ, IκBε, and Bcl-3). Upon stimulation, IκB becomes phosphorylated by the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, leading to IκB ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. With the degradation of IκB, the NF-κB complex is then freed to enter the nucleus to activate the transcription of target genes.
배송/결제/교환/반품 안내
배송 정보
| 기본 배송비 |
| 교환/반품 배송비 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 착불 배송비 |
| ||
| 교환/반품 배송비 |
| ||
결제 및 환불 안내
| 결제수단 |
|
|---|---|
| 취소 |
|
| 반품 |
|
| 환급 |
|
교환 및 반품 접수
| 교환 및 반품 접수 기한 |
|
|---|---|
| 교환 및 반품 접수가 가능한 경우 |
|
| 교환 및 반품 접수가 불가능한 경우 |
|
교환 및 반품 신청
| 교환 절차 |
|
|---|---|
| 반품 절차 |
|