
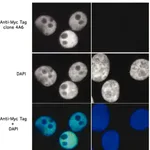
Merck Anti-Myc Tag Antibody, clone 4A6
✨AI 추천 연관 상품
AI가 분석한 이 상품과 연관된 추천 상품들을 확인해보세요
연관 상품을 찾고 있습니다...
Anti-Myc Tag Antibody, clone 4A6
clone 4A6, Upstate®, from mouse
Identification of the target epitope is important for characterization of a monoclonal antibodies. Epitope tags are short, linear antibody recognition sequences that enable detection of tagged fusion proteins by antibodies. Over the years, a wide range of anti-tag antibodies have been developed and each one of these offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Epitope tags can undergo post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation and glycosylation in cells and cause an increase in the molecular mass of the fused protein, which can result in changes in gel mobility. Epitope tags of smaller number of amino acid residues are advantageous in that they exhibit minimal side effects on structure and function of fused target protein. A Myc tag can be used in many different immunoassays and is useful when there is no antibody against the protein of interest. Adding a Myc-tag permits the detection of such proteins with an antibody against the Myc epitope. Clone 4A6 is an antibody that recognizes ten amino acid sequence EQKLISEEDL (Glu-Gln-Lys-Leu-Iso-Ser-Glu-Glu-Asp-Leu) corresponding to the C-terminal region of human c-Myc protein (UniProt: P01106). Unlike other clones whose performance may be affected when Myc tag sequence is followed by smaller neutral amino acids, Clone 4A6 offers much more consistent detection of Myc-tagged proteins irrespective of any changes in neighboring amino acid sequences. (Ref. Schuchner, S., et al. (2020). Sci. Signal. 13(616); eaax9730; Charest-Morin, X., et al. (2013). Front. Pharmacol. 4: 122).
🏷️Merck Sigma 상품 둘러보기
동일 브랜드의 다른 상품들을 확인해보세요
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-Actin antibody, Mouse monoclonal
888,800원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-CTCF Antibody
205,900원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-Myc Tag Antibody, clone 4A6
205,900원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST) antibody produced in rabbit
269,000원
Merck Sigma
Merck Monoclonal Anti-Neurofilament 200 (Phos. and Non-Phos.) antibody produced in mouse
255,400원
배송/결제/교환/반품 안내
배송 정보
| 기본 배송비 |
| 교환/반품 배송비 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 착불 배송비 |
| ||
| 교환/반품 배송비 |
| ||
결제 및 환불 안내
| 결제수단 |
|
|---|---|
| 취소 |
|
| 반품 |
|
| 환급 |
|
교환 및 반품 접수
| 교환 및 반품 접수 기한 |
|
|---|---|
| 교환 및 반품 접수가 가능한 경우 |
|
| 교환 및 반품 접수가 불가능한 경우 |
|
교환 및 반품 신청
| 교환 절차 |
|
|---|---|
| 반품 절차 |
|
