
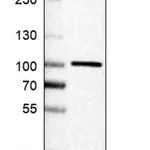
Merck Anti-Glutaredoxin-2 (Grx2)
✨AI 추천 연관 상품
AI가 분석한 이 상품과 연관된 추천 상품들을 확인해보세요
연관 상품을 찾고 있습니다...
Anti-Glutaredoxin-2 (Grx2)
from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography
Glutaredoxin-2, mitochondrial
Glutaredoxin-2, mitochondrial (UniProt: Q9NS18) is encoded by the GLRX2 (also known as GRX2, CGI-133) gene (Gene ID: 51022) in human. Glutaredoxin-2 is a glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase that is widely expressed and facilitates the maintenance of mitochondrial redox homeostasis upon induction of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Its active form is a monomer and it can dimerize to an inactive form where homodimers are linked by one 2Fe-2S cluster. The 2Fe-2S may serve as a redox sensor and the presence of one-electron oxidants or reductants can lead to the loss of the 2Fe-2S cluster and subsequent monomerization and activation of the enzyme. Glutaredoxin-2 acts as a very efficient catalyst of monothiol reactions because of its high affinity for protein glutathione-mixed disulfides. It can receive electrons not only from glutathione (GSH), but also from thioredoxin reductase supporting both monothiol and dithiol reactions. Glutaredoxin-2 is known to efficiently catalyze both glutathionylation and deglutathionylation of mitochondrial complex I, which in turn regulates the superoxide production by the complex. Overexpression of glutaredoxin-2 decreases the susceptibility to apoptosis and prevents loss of cardiolipin and cytochrome c release.
🏷️Merck Sigma 상품 둘러보기
동일 브랜드의 다른 상품들을 확인해보세요
Merck Sigma
Merck Monoclonal Anti-FUT4 antibody produced in mouse
613,400원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-α Actinin antibody, Mouse monoclonal
269,000원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-Glutaredoxin-2 (Grx2)
365,200원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) antibody produced in rabbit
225,000원
Merck Sigma
Merck Anti-APPL1
370,530원
배송/결제/교환/반품 안내
배송 정보
| 기본 배송비 |
| 교환/반품 배송비 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 착불 배송비 |
| ||
| 교환/반품 배송비 |
| ||
결제 및 환불 안내
| 결제수단 |
|
|---|---|
| 취소 |
|
| 반품 |
|
| 환급 |
|
교환 및 반품 접수
| 교환 및 반품 접수 기한 |
|
|---|---|
| 교환 및 반품 접수가 가능한 경우 |
|
| 교환 및 반품 접수가 불가능한 경우 |
|
교환 및 반품 신청
| 교환 절차 |
|
|---|---|
| 반품 절차 |
|
